SEQUENTIAL(CONTIGUOUS) FILE ALLOCATION
CONTIGUOUS ALLOCATION
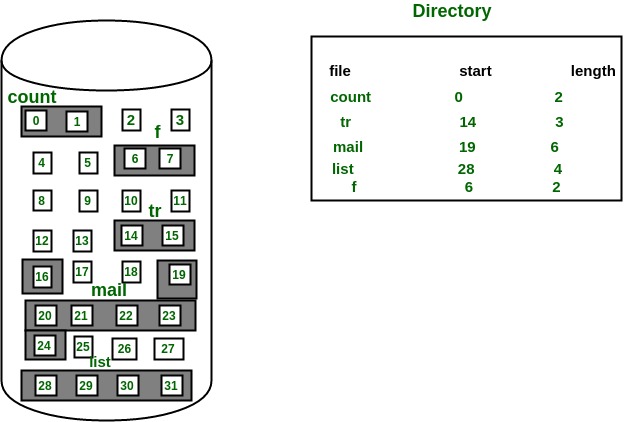
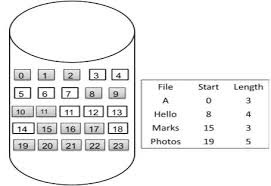
In this scheme, each file occupies a contiguous set of blocks on the disk. For example, if a file requires n blocks and is given a block b as the starting location, then the blocks assigned to the file will be: b, b+1, b+2,……b+n-1. This means that given the starting block address and the length of the file (in terms of blocks required), we can determine the blocks occupied by the file. The directory entry for a file with contiguous allocation contains Address of starting block Length of the allocated portion.
Advantages
Both the Sequential and Direct Accesses are supported by this. For direct access, the address of the kth block of the file which starts at block b can easily be obtained as (b+k). This is extremely fast since the number of seeks are minimal because of contiguous allocation of file blocks